QR codes have become a staple in our daily routines, making tasks like contactless payments and easy access to information simple and convenient. But how often do we consider the potential security risks that come with their widespread use? With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, QR codes are now being used by hackers as a stealthy method to bypass Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). This can happen so seamlessly that many don’t realize their data is compromised until it’s too late. For instance, when users scan a code and are directed to what seems like a legitimate login page, they’re actually submitting credentials into a trap set by cybercriminals. This emerging threat requires our attention and understanding, especially as organizations look to protect sensitive data from such clever exploits. Read more on how you can stay safe from quishing scams.
Understanding Quishing: A New Form of Cyber Attack
The surge in digital connectivity has gifted us unparalleled convenience, yet it also opens the floodgates to innovative cyber threats. Enter quishing—a novel variant of phishing that harnesses the humble QR code as its weapon of choice. As businesses and consumers increasingly rely on QR codes for swift transactions and information access, this threat demands immediate attention.
What is Quishing?

Photo by Tima Miroshnichenko
Quishing, short for “QR phishing,” is a malicious tactic exploiting QR codes to deceive users. Cybercriminals ingeniously embed harmful URLs within QR codes that, when scanned, redirect unsuspecting victims to phishing sites. The Check Point Software notes this clever adaptation poses a significant risk as it preys on users’ habitual trust in QR codes. With the prevalence of mobile scanning apps, these attacks are especially effective on devices lacking comprehensive security measures.
How Quishing Works
Quishing is intricately woven with social engineering, preying upon routine behaviors and the often unquestioned trust we place in QR codes. Attackers typically launch their attacks through:
- Deceptive Emails: Quishing emails resemble legitimate communications, often containing company logos and formal language. QR codes inserted within these emails lead recipients to malicious sites.
- Fake Websites: Once a QR code is scanned, users are transported to a meticulously crafted fake login page that mimics legitimate websites, like those of banks or services such as Microsoft 365.
- Urgency Triggers: Scammers often generate a sense of urgency, pressuring users to act quickly—such as warning of account expiries—intending to suppress critical thinking.
Be on the lookout for inconsistencies like non-matching file names or unusual email subject lines. Employing robust endpoint security protections and maintaining vigilance when scanning QR codes can lessen the risk of falling victim to these attacks. As we navigate this evolving digital age, understanding quishing becomes imperative, not only for safeguarding personal information but also for protecting organizational data from cunning exploits. Read more about how you can stay safe from quishing scams.
The simplicity with which quishing exploits our trust in technology highlights the importance of continuous vigilance and education on cybersecurity practices.
Real-World Example: Sophos Quishing Incident
In today’s digital age, QR codes are common and convenient, yet pose hidden threats like quishing, a cunning spin on phishing that can bypass Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). The recent quishing incident at Sophos serves as a stark reminder of vulnerabilities that exist, even within tech-savvy environments.
The Attack Scenario
Sophos found itself at the center of a sophisticated quishing attack. Employees received emails that appeared to be regular office correspondence, complete with company branding. The emails suggested a sense of urgency, instructing recipients to scan an embedded QR code to digitally sign an important document—disguised as needing a quick response due to an impending deadline.
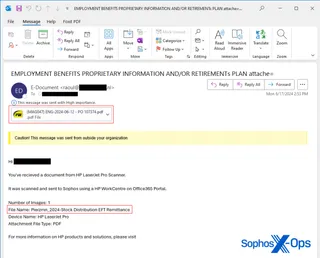
When scanned, these QR codes directed users to convincingly spoofed Office 365 login pages. Here, employees unwittingly entered their credentials, which were immediately captured by the attackers. This allowed them to exploit the stolen multi-factor authentication tokens to attempt unauthorized access to specific internal applications. Thanks to Sophos’ internal network security measures, further damage was averted just in time.
Read more about phishing attack prevention with Sophos solutions.
Impact on the Organization
Despite the potential for severe damage—loss of sensitive data, compromised systems, or reputational harm—the successful mitigation in this instance highlighted important lessons for Sophos and others. The rapid response to the detected breach underscored the importance of robust internal security protocols. It also emphasized employee awareness training as a vital component in the cybersecurity arsenal.
Organizations must learn from Sophos’ near miss. Employing comprehensive user training programs, such as those offered by Sophos Phish Threat, is crucial in teaching staff to recognize the subtle discrepancies typical of phishing attempts, thereby enhancing frontline defenses against cyber threats.
In the highly connected environments we operate today, vigilance and preparation are paramount. The Sophos quishing case isn’t just a story of threat detection and prevention, it’s a call to be ever aware.
Recognizing the Red Flags of Quishing Emails
Quishing emails are a sobering reminder of how adept cybercriminals have become in crafting deceptive messages that cleverly bypass standard security checks. Often disguised as legitimate communications, these emails carry the potential to trick even the most vigilant users. Understanding the traits of these emails is your first line of defense against this stealthy threat.
Common Characteristics of Quishing Emails
One of the key talents of cybercriminals is their ability to mimic trusted sources. Let’s explore some common traits that can help you spot a quishing email:
- Mismatched Email Details: Check if the sender’s address aligns with their organization. Often, subtle typos or extra characters are red flags.
- Urgent Language: These emails may claim dire consequences if immediate action isn’t taken. This tactic is used to suppress critical thinking.
- Unexpected Attachments or Links: Be wary of emails with QR codes or links where you did not anticipate them. Legitimate enterprises typically do not send unsolicited attachments with QR codes.
- Generic Greetings and Grammar Mistakes: If the email lacks personalization and contains grammatical errors, it’s likely designed to target a broad audience, not you specifically.
- False Sense of Urgency: Scammers often impose tight deadlines or imply account suspensions to rush you into compliance.

Photo by Andrea Piacquadio
Best Practices for Email Security
Awareness is your strongest ally in email security. By adopting thoughtful practices, you can significantly decrease your exposure to quishing threats:
- Verify Before You Trust: Always verify the sender’s identity before responding or scanning any QR code.
- Utilize Security Software: Employ reliable endpoint security solutions that can identify and block suspicious emails and attachments. Regularly update this software to keep up with evolving threats.
- Educate and Train: Regular training programs for employees can empower them to recognize red flags associated with quishing and other phishing attacks. These programs should be a staple in your organizational security strategy.
For more comprehensive strategies on safeguarding against such attacks, consider exploring resources like Microsoft’s guide on phishing protection.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): While quishing can target MFA, it’s still a critical layer of defense. Ensure your MFA implementations are up-to-date to thwart unauthorized access.
- Regularly Update Software: Software updates often include vital security patches. Ensure your systems are current to mitigate exposure to vulnerabilities.
- Report Suspicious Emails: Encourage a culture of reporting within your organization. If something seems off, it likely is. Prompt reporting can prevent widespread damage.
Staying informed and prepared can significantly minimize the risk of falling prey to quishing attacks. By integrating these practices into your daily routine, you’re not just defending your inbox, but fortifying your digital life against potential intruders.
For more information on securing your organization from these threats, read how to recognize and avoid phishing scams.
How to Protect Against Quishing Attacks
The rise of quishing attacks, where malicious actors use QR codes to launch phishing schemes, underscores the critical need for robust defense strategies. These threats exploit our trust in familiar technologies, making them particularly stealthy. Protecting against such attacks requires a multifaceted approach, integrating strong multi-factor authentication protocols and continuous user education.
Implementing Stronger MFA Protocols

Photo by cottonbro studio
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) serves as a cornerstone in safeguarding digital identities. But, as quishing showcases, even MFA can be vulnerable. To ensure its effectiveness:
- Adopt Adaptive Authentication: This method tailors the verification process based on user behavior and context, raising flags when anomalies are detected.
- Opt for Stronger Authentication Factors: Beyond passwords and SMS codes, employ biometric verification or app-based authenticators.
- Keep Systems Updated: Regular updates to authentication platforms are crucial to close potential security gaps. For more insights, check Microsoft’s guidelines on phishing protection.
These enhancements ensure that even if one layer is compromised, additional hurdles will deter unauthorized access.
User Education and Training
Human vulnerability often becomes the easiest target for cybercriminals. Investing in user education and training is not just a recommendation, but a necessity:
- Host Regular Training Sessions: These should cover the latest threat tactics and how to spot them.
- Simulated Phishing Exercises: Engage employees with realistic drills to test their readiness against actual attacks.
- Implement Feedback Loops: Encourage users to report suspicious activities and reward proactive behavior to foster a vigilant culture.
User education equips teams with the knowledge to recognize deceptive tactics, such as those detailed in this guide, making them an integral line of defense against cyber threats.
In the battle against quishing, fortified MFA systems and a well-informed workforce act as a formidable defense. Staying updated and reactive to evolving threats is the key to maintaining your organization’s security posture.
The Future of QR Codes in Cybersecurity
QR codes have become ubiquitous tools in our digital toolkit, seamlessly blending into our everyday tasks from accessing menus to securing online payments. Yet, as their use becomes more prevalent, so do the opportunities for cyber threats to exploit this technology. In the domain of cybersecurity, the question now arises: how can we harness QR codes while ensuring they remain a secure conduit for data?
Potential Innovations to Improve QR Code Safety

Photo by Ron Lach
As we look to the future, the landscape of QR technology is poised for several advancements. By anticipating these changes, we can build a safer infrastructure for QR code usage. What might these innovations look like?
- Embedded Verification Protocols: Just as emails often come with domain verification, QR codes could evolve to include embedded security protocols ensuring the authenticity of the source. This could involve a digital signature or a similar verification process, providing a layer of trust before any link is opened.
- Biometric Security Measures: Utilizing biometric verification, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, before allowing QR code access might become a standard practice. This adds a personal security barrier, making it harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain technology could serve as a tamper-resistant ledge for QR codes, recording every scan and providing an auditable trail. This would not only enhance security but also increase transparency in transactions involving QR codes.
For more insights into potential technological shifts, you might find this article by Trend Micro enlightening, as it delves into the dual nature of QR codes as both tools of convenience and potential cyberthreats.
Regulatory Changes and Compliance
As QR codes become embedded in more facets of our digital interactions, regulatory bodies will likely step up to ensure these systems do not become avenues for cybercrime. This means potential changes in compliance requirements and industry standards could emerge to safeguard users.
A few potential regulatory changes we might anticipate include:
- Standardized Security Requirements: New regulations may call for standardized security practices for all QR code generators and readers, potentially requiring encryption or mandatory security features in QR code systems.
- Privacy-Focused Regulations: As with GDPR in the European Union, privacy concerns could spur regulations ensuring QR data isn’t misused or shared without consent. This might involve guidelines on how QR code data is stored and who can access it.
- Mandatory Security Disclosures: Manufacturers and service providers using QR codes may be required to provide clear disclosures about the security of their codes and the risks involved, similar to the way cookies and trackers are notified currently.
The challenges and opportunities in QR code regulation are substantial and require agencies to be proactive in closing potential loopholes. Articles like Cybersecurity Concerns with QR Codes discuss these evolving concerns and how critical it is for regulatory bodies to stay ahead of threats.
QR codes are more than just a digital convenience; they represent a significant part of our interaction with the digital world. By leveraging innovation and understanding regulatory progress, we can ensure they evolve into tools that enhance, rather than threaten, our security landscape.
Conclusion
QR codes have become indispensable in our connected world, yet this convenience comes with risks. As seen with quishing, hackers exploit these codes to bypass security measures like multi-factor authentication. The key takeaway is simple: be vigilant.
Double-check URLs before entering credentials. Companies must bolster cyber defenses and train employees regularly on spotting scams. This proactive approach can turn potential targets into informed defenders.
Stay informed, stay safe. It’s crucial to remain alert against innovative threats. Let’s keep our digital lives secure and protected.


